07-07-2024 - Energy systems - Steam generator[EN]-[IT]

~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
07-07-2024 - Energy systems - Steam generator[EN]-[IT]
Steam generator
notes and sketch
The steam generator is what is more commonly called a boiler.
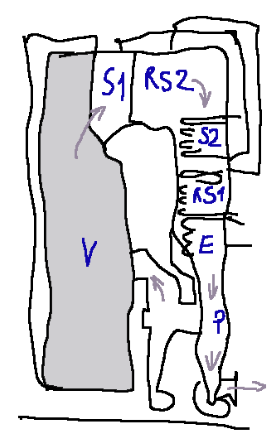
Here we follow the diagram of a tube boiler
Below is the relevant heat exchange diagram
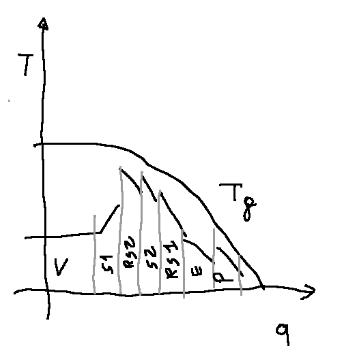
NOTE 1:
The boilers currently used in electrical production plants use direct heat radiation from the firebox to the water pipes, allowing high specific steam production.
NOTE 2:
Based on the method of installation, the boilers are divided into fire tube boilers and water tube boilers
Function of the components of a steam generator
Sequence operation:
-The first section of the boiler to be crossed by the water is the economizer.
We can say that the economizer collects waste heat from the exhaust gases before they leave the boiler, pre-heating the feed water to improve efficiency.
-At the economizer outlet the water is conveyed, via connection pipes, to the vaporizer circuit.
-The vaporizer (or evaporator) is installed in the combustion chamber, where the highest gas temperature and the most intense heat exchange are found.
-The cylindrical body has the function of separating the steam, produced in the screen tubes, from the liquid which descends again into the drop tubes to begin a new path in the vaporizer
-Superheater. From the vaporizer it passes into the superheater, which has the purpose of raising the temperature of the steam at constant pressure, in order to achieve a greater enthalpy difference in the turbine.
In summary the superheater further heats the generated steam above its boiling temperature to improve the efficiency of the cycle.
-The resuperheater is made up of banks of coils and is generally placed in the horizontal gas duct, after the banks of the final superheater.
-the preheater (last exchanger) used to preheat the air entering the burner. The preheater has the task of heating the combustion air at the expense of the heat contained in the fumes at the boiler outlet
Acid Dew
The phenomenon of acid dew in a boiler occurs due to the condensation of corrosive acids from the combustion gases. If the fumes are cooled below the dew point temperature, acid dew forms, resulting in corrosion problems on the walls of the heat exchangers.
We remind you that when a fuel containing sulfur (even in minimal percentages) is burned in the steam generator, sulfuric acid is also found in the fumes, together with the water vapour.
Conclusions
The complex sequence of components of a boiler is designed to transform the chemical energy of the fuel into thermal energy.
Request
Did you imagine that a boiler was actually so complex?

ITALIAN
07-07-2024 - Sistemi energetici - Generatore di vapore[EN]-[IT]
Generatore di vapore
cenni e schizzo
Il generatore di vapore è quello che più comunemente viene chiamato caldaia.
Qui si seguito lo schema di una caldaia a tubi

Qui di seguito il relativo diagramma di scambio termico

NOTA 1:
Le caldaie attualmente utilizzate negli impianti di produzione elettrica utilizzano l'irraggiamento diretto del calore dal focolare ai tubi d'acqua consentendo elevate produzioni specifiche di vapore.
NOTA 2:
In base al modo di installazione le caldaie vengono distinte in caldaie a tubi di fumo e caldaie a tubi d'acqua
Funzione dei componenti di un generatore di vapore
Funzionamento in sequenza:
-La prima sezione di caldaia ad essere attraversata dall’acqua è l’economizzatore.
Possiamo dire che l'economizzatore raccoglie il calore residuo dai gas di scarico prima che lascino la caldaia, pre-riscaldando l'acqua di alimentazione per migliorare l'efficienza.
-All’uscita dell’economizzatore l’acqua viene convogliata, mediante tubi di collegamento, al circuito vaporizzatore.
-Il vaporizzatore (o evaporatore) viene installato in camera di combustione, dove si trova la più alta temperatura dei gas e lo scambio termico più intenso.
-Il corpo cilindrico ha la funzione di separare il vapore, prodotto nei tubi schermo, dal liquido che scende nuovamente nei tubi di caduta per iniziare un nuovo percorso nel vaporizzatore
-Surriscaldatore. Dal vaporizzatore si passa nel surriscaldatore, che ha lo scopo di innalzare la temperatura del vapore a pressione costante, in modo da realizzare un maggiore salto entalpico in turbina.
In sintesi il surriscaldatore riscalda ulteriormente il vapore generato oltre la sua temperatura di ebollizione per migliorare l'efficienza del ciclo.
-Il risurriscaldatore è formato da banchi di serpentine ed è generalmente sistemato nel condotto orizzontale dei gas, dopo i banchi del surriscaldatore finale.
-il preriscaldatore (ultimo scambiatore) utilizzato per preriscaldare l’aria in ingresso al bruciatore. Il preriscaldatore ha il compito di riscaldare l’aria comburente a spese del calore contenuto nei fumi all’uscita della caldaia
Rugiada acida
Il fenomeno della rugiada acida in una caldaia si verifica a causa della condensazione di acidi corrosivi dai gas di combustione. Se i fumi vengono raffreddati al di sotto della temperatura di rugiada, si ha formazione di rugiada acida, con conseguenti problemi di corrosione sulle pareti degli scambiatori di calore.
Ricordiamo che quando nel generatore di vapore viene bruciato un combustibile contenente zolfo (anche in percentuali minime), nei fumi, insieme al vapore d’acqua, si trova anche acido solforico.
Conclusioni
La sequenza complessa dei componenti di una caldaia è stata ideata per trasformare l'energia chimica del combustibile in energia termica.
Domanda
Lo immaginavate che una caldaia in realtà fosse così complessa?
THE END
L'economizzatore in realtà è alla base del principio delle caldaie a condensazione @tipu curate 2
Upvoted 👌 (Mana: 45/65) Liquid rewards.
The acid dew phenomenon and its impact on boiler efficiency are pretty interesting bro
I never knew a boiler could be so complex
Thanks for explaining this course
Ooh
I wish I could just loosen the boiler in my house to check some of these things
Nice one!