Salmonella Typhi; The Silent Killing Bacteria
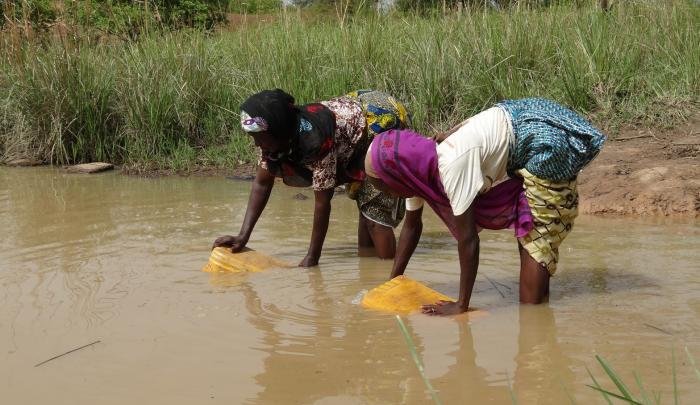
In Nigeria, if you are diagnosed with malaria, there is a high chance with would be diagnosed with typhoid especially when you go to health centers that are not well equipped. Malaria is quite common here and typhoid in places where people consume contaminated water but why will I be consuming treated water and cook with treated water and still fall sick after multiple and numerous bites only to be diagnosed with Malaria and Typhoid when I went to a clinic nearby since I was so weak to go to a big hospital.
After the diagnosis, I was forced to go to a bigger and better hospital for a test where the widal test showed something different and better. I am not saying it is not possible not to have typhoid even when drinking packaged water, my suggestion is that you get tested properly. That said, I want to discuss Typhoid fever and I hope we all enjoy this post.
Typhoid fever is a bacteria infection that is basically caused by the ingestion of contaminated food, water, or even sewage. This bacteria Salmonella typhi can cause holes in the intestine, infecting other organs in the body and this bacteria is becoming drug resistant in recent times. The Salmonella typhi is completely different from the food-borne salmonellosis which is transmitted by the consumption of infected raw animals or egg, Typhoid affects humans, and the bacteria is able to live outside its hosts body till it is picked up again by a potential host.
Salmonella after ingestion goes straight to the stomach and in healthy people, the gastric acid in the stomach can kill the bacteria but this case is different for children and adults who do not produce enough stomach acid leaving them susceptible to the bacteria infection. Once they are not killed in the stomach, they find their way into the small intestine and start to function in the cells lining the intestine.
Just as expected, your body immune system triggers the inflammatory immune response so as to fight the bacteria and in this process, it can lead to the puncture of the lining of the intestine leading to ulceration. This can lead to gastric content entering into the abdomen gradually. The bacteria then find its way to the lymphoid tissue known as peyer's patches which are part of the gut-associated lymphoid tissue underlying the enterocytes.
From here they go into the bloodstream, reaching different organs in the body especially the liver, spleen and bone marrow. They also go to the large intestine after which they are excreted through feces. In some cases, the typhoid bacteria also cause ulceration in the peyer's patches down to the outer lining of the terminal ileum thereby reaching the small intestine leading to the perforation of the small intestine. This can be deadly if an open surgery is not done as soon as possible and it can spread to the heart, the brain, the pancreas and the heart, and can lead to complications like pancreatitis, meningitis, other problems in the body. Other symptoms can range from headache loss of appetite, diarrhea, and rash.
When the bacteria is excreted into sewage, they can find their way water in non-hygienic places in what s known as fecal-oral route of transmission. The bacteria is very clever and it lives inside macrophages cell thereby evading the immune system but then, this bacteria can be combated with antibiotics although it is now becoming resistant to some antibiotics and they are known as Extensively Drug Resistant Salmonella typhi or XDR type of typhoid. In some cases, after the bacteria has been combated, they can stay in the gall bladder and hide there where they are excreted with feces and the people become carriers such as in the case of Typhoid Mary.
Accurate diagnosis and proper treatment are crucial in managing diseases like malaria and typhoid fever. While both diseases are common in regions like Nigeria, ensuring clean water and proper hygiene can help reduce the risk of typhoid fever. It’s essential to seek medical care from well-equipped health centers to receive accurate diagnoses and effective treatments, especially given the rising threat of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Reference
https://www.nytimes.com/2017/09/28/health/typhoid-vaccine-trial.html
https://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJM197009242831306
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3959940/
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/typhoid
https://www.ajtmh.org/view/journals/tpmd/104/5/article-p1755.xml
https://emergency.cdc.gov/han/pdf/CDC-HAN-439-XDR

Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.